>
Blog>
Electronic Control Units ExplainedElectronic Control Units Explained
In many ways, the electronic control unit can be considered the most important component in a modern car, through it all primary functions operate. Below we take a look at exactly what it does, and what issues it can cause.
What does ECU stand for?
The acronym ECU refers to a car's Engine Control Unit, there are many other control units in modern cars such as:
- ECM - Engine Control Module
- ECU - Engine Control Unit
- TCM - Transmission Control Module
- BCM/BCU - Body Control Module/Unit
- GCM/GCU - Gearbox Control Module/Unit
- ABSM - Anti Lock Braking Module
What is an Electronic Control Unit
As the name suggests, the ECU is a device that controls and monitors various parameters and systems in a car. The first ECUs were basic microprocessors that only monitored basic engine parameters such as fuel injection, timing and ignition.
With the advent of things such as electric windows and doors, reversing cameras and parking sensors, modern cars have multiple control units alongside the ECU, such as Body control modules, lighting modules and more.
All of these fulfil the same function within their respective system, to control and display data about the car’s status, either changing parameters or displaying issues to the driver.
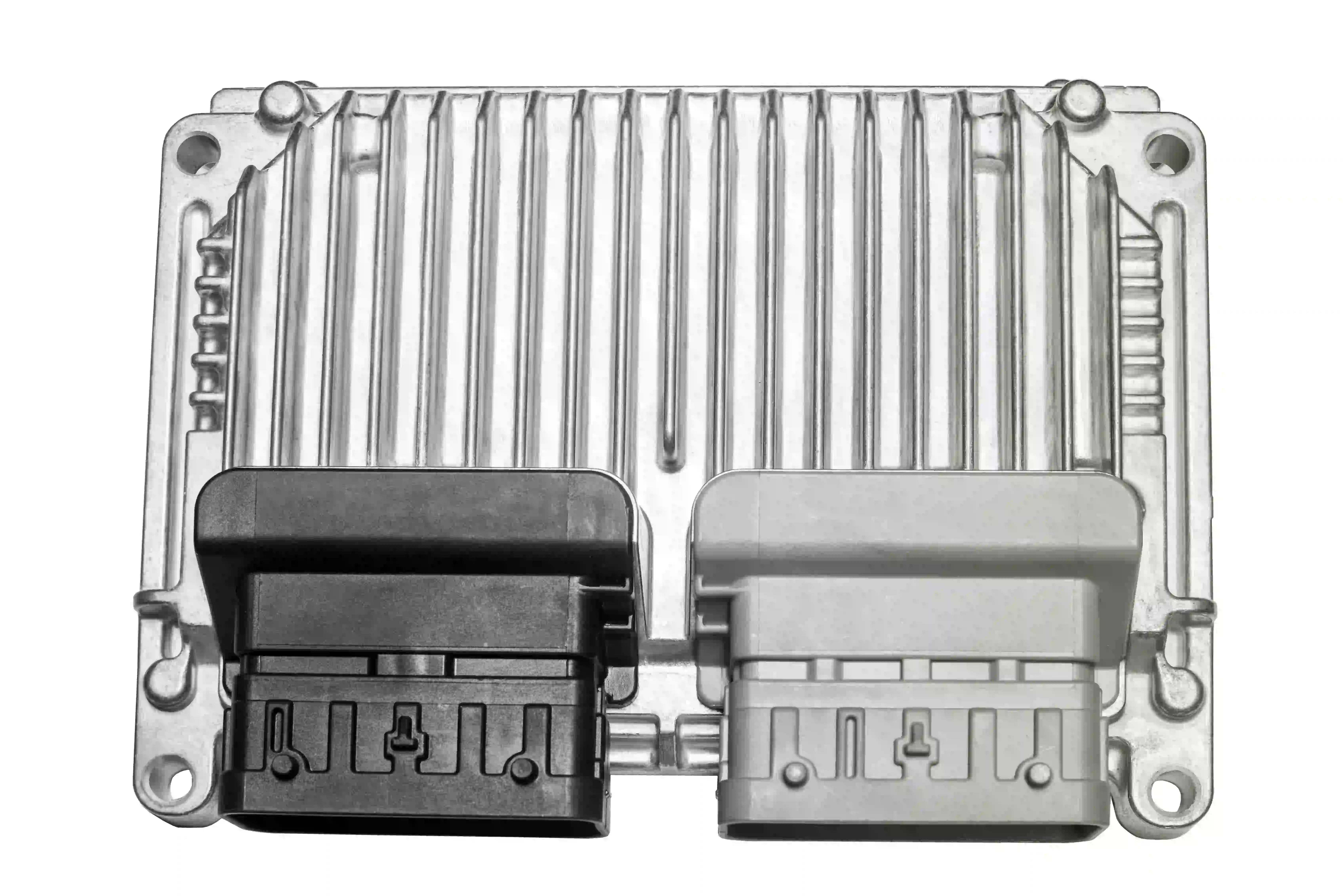
What does an ECU do?
Modern ECUs control or read almost everything that happens in and around the engine. There is a plethora of sensors that report back and parameters, of which the ECU will regulate, monitor and take action.
For instance, the ECU uses data from the engine on RPM, Ignition timing, fuel injection rates and exhaust gas composition, to detect whether the combustion is happening exactly as it should.
In the instance of any faults, such as a misfire, the ECU will detect and make changes accordingly, whether that is to alter the ignition timing or display an error message to the driver.
Other control units such as body-control units monitor the status of things such as bulbs, windows, door locks, wiper motors and more. Again allowing the car to display an error message to the driver.
How many ECUs does a car have
Typically a modern car will have around 4 different ECUs; including the engine control unit, body control unit, ABS control unit and alarm/immobiliser control unit.
But luxury cars will often have even more than this, with some vehicles having a separate unit to control things such as infotainment systems, active aerodynamics and more.
What causes ECU failure?
The most common cause of ECU damage, especially in the UK, is water damage. A lot of manufacturers mount the ECU near the passenger or driver footwell, as this is convenient for all the electrical systems whilst being protected from the elements.
However, the elements can sometimes get into this area, as things such as car sunroofs, windows and windscreens can leak. The water can then run down into the footwell and damage the ECU.
Another common cause of ECU damage is faulty or badly modified electrical systems, such as shorts and wiring issues. Jump starting incorrectly can also cause problems, as high electrical loads can be sent through the ECU.
Some cars can suffer if the battery is left to drain to empty too often or for too long, damaging the ECU’s internal battery system.
What is an ECU remap?
One of the main jobs the ECU does is control the fueling and ignition of the engine. On fuel-injected cars, this means the ECU can increase or decrease the amount of fuel injected, and on turbocharged cars, the amount of turbo pressure is permitted.
An ECU remap is the process of adjusting the parameters to which the ECU adjusts fueling, timing and turbo pressure to produce more power. They can also be adjusted to increase the efficiency of the engine if required.
ECU remaps achieve the best results on turbocharged cars, where the horsepower can often be increased by more than 50%, but care should be taken to longevity and also any insurance, finance or servicing requirements when doing this.
Can an ECU be repaired?
In many cases, the ECU will be damaged beyond repair, but it’s always worth looking into specialist independent repair services. These often exist for more niche and rare collector cars, where replacement parts are not readily available.
After an ECU has sustained damage, it will usually cause many issues with the running of the car, if the main ECU has been damaged in any way, it will often cause the car to fail to start completely.
If it can be repaired, depending on the severity and complexity of the ECU, it could cost between £200 - £500 to repair.

How much does a replacement ECU cost?
If your ECU is damaged beyond repair, you’ll need to replace it with a like-for-like part. This can be expensive in certain circumstances. Complete ECU replacements can cost between £300 and £2,000 for the parts and labour.
Whilst the parts can be quite expensive, in the region of £300-£600 for a regular car, the labour, speciality software, and tools required can often be the main cost.
The main issue to be found is that many control modules on modern cars are digitally keyed to other parts of the car, such as immobilisers, ignition barrels, door locks and such. In some cases, an ECU needs to be sold as a set, alongside immobilisers and ignition barrels.
If you need some assistance with covering the cost of an ECU repair, split the bill with Bumper, completely interest-free, and find a local service partner to carry out your repair.
Author - Joseph Law
Joseph has been writing about cars for over seven years and writing for Bumper for over two, blending his passion for automobiles with a talent for storytelling.
Joseph has written about engineering and cars for Autozilla, Komaspec, and several engineering manufacturers. When he's not writing or tinkering with one of his five cars, Joseph dreams of owning an Alfa Romeo 33 Stradale.
Related Posts